- Docs
- /
Comparisson between SQL services on Azure
25 Feb 2021 40256 views 0 minutes to read Contributors ![]()
Introduction
Azure SQL is a family of fully managed, secure, and intelligent SQL database services that support a wide range of application patterns, from re-hosting and modernizing existing SQL Server workloads to modern cloud application development.
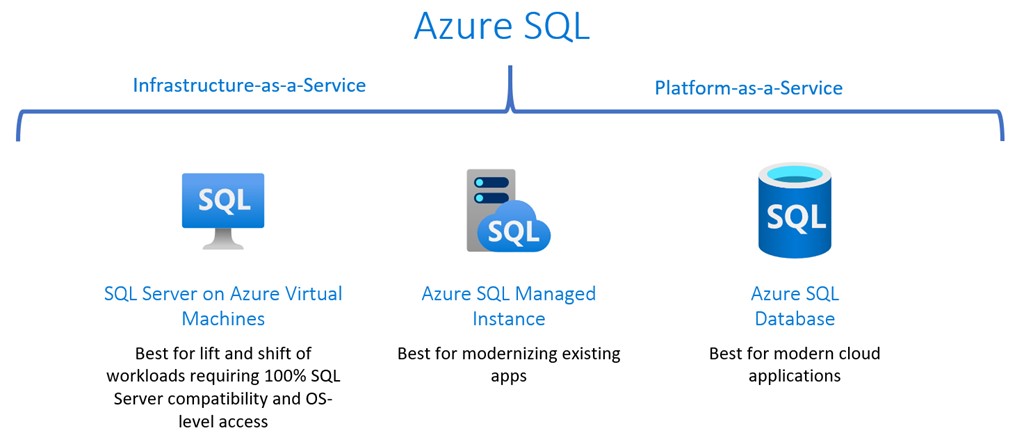
Because the entire Azure SQL family is built upon the same SQL Server database engine, you can migrate applications with ease and continue to use the tools, languages, and resources you’re familiar with. You’ll discover that your skills and experience transfer easily to the cloud, as the innovative features in Azure SQL help you operate more efficiently and save money along the way.
The question is, how do we can help your customers choose the right option for their needs? This is an area where partners can add value for customers. We can help them make a choice that will solve the challenges they may be facing today, with flexibility to address their future business needs as well.
So we brought up below comparison together so our customer can understand and chose right type of SQL service on Azure.
Azure SQL Database vs SQL Server on Azure VMs
|
Azure SQL Database |
Azure IaaS SQL Server |
|
|
|
|
Database Features |
The majority of the database-level features, SQL standards, T-SQL query processing are supported. For example, database collation, database auditing, T-SQL Expression, etc. |
It supports all the SQL Server on-premises capabilities |
|
|
|
Database size |
1. The database size is always based on the underlying service tier models. For example, the Premium P15 service tier model supports up to 4 TB databases 2. Azure SQL Database support databases of up to 100 TB with the Hyperscale service tier model 3. Databases per logical server are 5000 4. DTU (Database Transaction Units) or eDTU (Elastic Database Transaction Units) quota is 54,000 per server
|
Max database size is constrained by the size of the VM. SQL Server instances support up to 256 TB of storage. The instance can support as many databases as needed For example, a premium storage disk can support up to 32 TB. You also have an option to use Ultra disk. The Ultra Disk is available in different sizes that can be customized for the range of input values You can refer to the Image 1 for more details |
|
|
|
Database File layout |
Multiple log files are not supported |
Multiple log files are supported |
|
|
|
Compute resources |
The computing resource is based on the DTU or VCore Model. There is no direct control over computing resources. You need to understand the performance baseline benchmarks to decide the computing |
In this case, you have full control over the VM compute resources for all the SQL Server deployments The VM series are broadly classified to fulfill all the application needs:
|
|
|
|
Availability |
It is 99.995% available and availability is guaranteed 1. By default, Azure infrastructure provides fault-tolerance and high Availability for the Azure SQL databases 2. By default, SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance store data in geo-redundant (RA-GRS) storage blobs that are replicated to a paired region 3. You can test the in-built automatic failover feature Invoke-AzSqlDatabaseFailover -ResourceGroupName 4. Also, you have active geo-replication and point-in-time restore of the databases |
The availability is up to 99.99% 1. By default, Azure infrastructure provides fault-tolerance and high Availability for the VMs 2. You can use SQL level high-availability and Disaster-recovery features 3. Achieving high-availability always incur the cost and additional overhead to manage the additional VM servers |
|
|
|
Migration |
It will be migrated to the latest available stable database engine version Run Database migration Assistant or Azure Migrate tools to define the upgrade or migration paths You can also try Transactional Replication in some cases You can refer to this article for T-SQL differences |
It will be a lift-and-shift kind of migration, if it is the same version You can use SQL native backup and restore method, log shipping, AlwaysOn for the migration |
|
|
|
Database Backup |
Automatic. It will support short-term (7 or 35 days) and Long-term up to 10 years based on the service tiers It is possible to restore the deleted database point-in-time, or to the earlier point-in time on the same server
|
It is not an automatic process. The database backups are managed using SQL native or any third-party tools |
|
|
|
Resource Management |
We have a scale in and scale out option to manage the compute (DTU) to individual databases |
You can still use the resource governance features with a heavy administration overhead |
|
|
|
Database Patching |
Automatic |
Manual |
|
|
|
License |
Built-in license model. The database software is automatically patched and upgraded by Microsoft 1. No upfront cost 2. Pay-As-You-Go — pay only for what you use |
Azure Hybrid Benefit (AHB)—It supports the use of the existing server license with Software Assurance BYOL (Bring-Your-OWN-License) model where you need to pay for VM (Compute) and storage only You also have the option to use Microsoft controlled licenses for SQL Server images versions such as SQL Server 2008R2, SQL Server 2012, SQL Server 2014, SQL Server 2016, SQL Server 2017, SQL Server 2019 and editions such as Developer Edition, Express Edition, Web Edition , Standard Edition, and Enterprise Edition Pay-as-you-go model Disaster recovery (DR) model where it is used only for DR in Azure |
|
|
|
Pricing |
Azure SQL Database pricing calculator |
|
|
|
|
Monitoring and Reporting |
Integrated with BI. It is easy to integrate with SQL Server analytics solution and Log Analytics using OMS |
Need integration with custom scripts or third party tool |
|
|
|
Usage |
1. High Time-to-market 2. Support modern lightweight application 3. In most cases, the agile application is built on this framework 4. Applications that need built-in high-availability, disaster recovery, and auto-patching and upgrade mechanisms 5. The application that requires automatic scale option |
1. Application requires minimal or no code changes usually prefer this type of infrastructure. This is usually because of application dependency and complex integration 2. OLTP databases where workload and transactions are managed and isolated independently 3. Security — the requirement is to get exclusive access or administrator privileges to the server 4. Scale up or down is available at the VM level, but some of them can be done online. In some cases, the VM needs to be brought down. For example, changing the disk type from Premium SSD to HDD |
|
|
|
SQL Agent, Linked server & DB Mail |
No SQL agent or DB mail or Linked server |
SQL Agent & DB Mail are supported as similar to on-premise. Supports Linked server |
|
|
|
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) |
By default, TDE is enabled |
TDE is not enabled by default. You need to walk-through the manual process to enable TDE manually |
|
|
|
Database Restore |
You can only restore using the Azure portal, or Azure PowerShell cmdlets or Azure CLI cmdlets Database restores with automated backups using SSMS is not allowed. Point-in-time database restores are possible and are performed using the above-mentioned set of methods |
Restore can be performed using SSMS and point -in-time restore possible depending on the backup frequency and database recovery model |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Database Copy |
Bacpac files, import/export or data copy methods to copy the databases |
Backpac, import/export, backup and restore method |
|
|
|
Business Intelligence Services |
Azure Data Factory (For SSIS packages) |
Power BI for SSRS ( SQL Server Reporting Services) |
|
|
|
Azure Analysis Services (for OLAP models) |
SSAS ( SQL Server Analysis Services) |
|
||
|
Recovery model |
Only Full Recovery that guarantees high availability is supported. Simple and Bulk Logged recovery models are not available |
All 3-recovery models Full, Simple, and Bulk-logged recovery models are supported |
|
|
|
Transactional Replication |
Yes, Transactional and snapshot replication subscriber only |
Replication is supported |
|
|
|
Driver and tool support |
It supports the following drivers: .Net Framework , ODBC, PHP, JDBC, OLEDB, NODE.js Tools: SSMS, sqlcmd, Azure Data Studio, MSSQL CLI You can refer to image 3 for more details |
SQL Server connectivity can be made using the following drivers: ODBC Drivers or SQL Native Client driver or OLEDB provider for SQL Server Tools: SSMS, sqlcmd, Azure Data Studio, MSSQL CLI |
|
Azure SQL Database vs Azure SQL Managed Instance
|
Feature |
Azure SQL Database |
Azure SQL Managed Instance |
|
Yes - see Cert store and Key vault |
Yes - see Cert store and Key vault |
|
|
99.99-99.995% availability is guaranteed for every database. Disaster recovery is discussed in Overview of business continuity with Azure SQL Database |
99.99.% availability is guaranteed for every database and can't be managed by user. Disaster recovery is discussed in Overview of business continuity with Azure SQL Database. Use Auto-failover groups to configure a secondary SQL Managed Instance in another region. SQL Server instances and SQL Database can't be used as secondaries for SQL Managed Instance. |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
Yes, with some differences |
||
|
Yes. Azure AD users only. |
Yes. Including server-level Azure AD logins. |
|
|
No, only system-initiated automatic backups - see Automated backups |
Yes, user initiated copy-only backups to Azure Blob storage (automatic system backups can't be initiated by user) - see Backup differences |
|
|
Most - see individual functions |
Yes - see Stored procedures, functions, triggers differences |
|
|
Yes, but just from Azure Blob storage as a source. |
Yes, but just from Azure Blob Storage as a source - see differences. |
|
|
Yes, without access to file system for BACKUP and CREATE operations. |
Yes, without access to file system for BACKUP and CREATE operations - see certificate differences. |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
No, default server collation SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS is always used. |
Yes, can be set when the instance is created and can't be updated later. |
|
|
Yes |
||
|
No |
Yes, but without access to file system in CREATE ASSEMBLY statement - see CLR differences |
|
|
Yes, but only database scoped credentials. |
Yes, but only Azure Key Vault and SHARED ACCESS SIGNATURE are supported - see details |
|
|
No - see Elastic queries |
Yes, plus Elastic queries |
|
|
No |
Yes, within the instance. See Linked server differences for cross-instance queries. |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
No |
||
|
No |
No |
|
|
Most - see individual statements |
Yes - see DBCC differences |
|
|
Most - see individual statements |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
Database only |
Yes |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
No - see Elastic transactions |
No - see Linked server differences. Try to consolidate databases from several distributed SQL Server instances into one SQL Managed Instance during migration. |
|
|
Most - see individual statements |
Yes |
|
|
Most - see individual DMVs |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
Elastic query (in public preview) |
Yes, with required RDBMS type. |
Yes, with required RDBMS type. |
|
No - see Alerts |
No |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Some - see Extended events in SQL Database |
Yes - see Extended events differences |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
Primary file group only |
Yes. File paths are automatically assigned and the file location can't be specified in ALTER DATABASE ADD FILE statement. |
|
|
No |
||
|
Yes, but third-party word breakers are not supported |
||
|
Most - see individual functions |
Yes - see Stored procedures, functions, triggers differences |
|
|
Yes in Premium and Business Critical service tiers. |
||
|
Most - see individual elements |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
No - see Elastic query |
Yes. Only to SQL Server and SQL Database without distributed transactions. |
|
|
Linked servers that read from files (CSV, Excel) |
No. Use BULK INSERT or OPENROWSET as an alternative for CSV format. |
No. Use BULK INSERT or OPENROWSET as an alternative for CSV format. Track these requests on SQL Managed Instance feedback item |
|
High availability is included with every database. Disaster recovery is discussed in Overview of business continuity. |
Natively built in as a part of Azure Data Migration Service migration process. Not available as High availability solution, because other High availability methods are included with every database and it is not recommended to use Log-shipping as HA alternative. Disaster recovery is discussed in Overview of business continuity. Not available as a replication mechanism between databases - use secondary replicas on Business Critical tier, auto-failover groups, or transactional replication as the alternatives. |
|
|
Yes, but CREATE and ALTER login statements do not offer all the options (no Windows and server-level Azure Active Directory logins). EXECUTE AS LOGIN is not supported - use EXECUTE AS USER instead. |
Yes, with some differences. Windows logins are not supported and they should be replaced with Azure Active Directory logins. |
|
|
No, only Full Recovery model is supported. |
No, only Full Recovery model is supported. |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
Yes, only to SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server. See T-SQL differences |
|
|
No |
Yes, only to SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server. See T-SQL differences |
|
|
Yes, only to import from Azure Blob storage. |
Yes, only to SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server, and to import from Azure Blob storage. See T-SQL differences |
|
|
Most - see individual operators |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
No. You can query data in the files placed on Azure Blob Storage using OPENROWSET function or use an external table that references a serverless SQL pool in Synapse Analytics. |
No. You can query data in the files placed on Azure Blob Storage using OPENROWSET function, a linked server that references a serverless SQL pool in Synapse Analytics, or an external table (in public preview) that references a serverless SQL pool in Synapse Analytics or SQL Server. |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
Machine Learning Services(Formerly R Services) |
Yes, in public preview |
No |
|
Only Full Recovery that guarantees high availability is supported. Simple and Bulk Logged recovery models are not available. |
Only Full Recovery that guarantees high availability is supported. Simple and Bulk Logged recovery models are not available. |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
No |
Yes, with mandatory FROM URL options for the backups files placed on Azure Blob Storage. See Restore differences |
|
|
From automated backups only - see SQL Database recovery |
From automated backups - see SQL Database recovery and from full backups placed on Azure Blob Storage - see Backup differences |
|
|
No. Use BACPAC or BCP instead of native restore. |
No, because SQL Server database engine used in SQL Managed Instance has higher version than any RTM version of SQL Server used on-premises. Use BACPAC, BCP, or Transactional replication instead. |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
Yes, but only within the instance. If you are using remote Service Broker routes, try to consolidate databases from several distributed SQL Server instances into one SQL Managed Instance during migration and use only local routes. See Service Broker differences |
|
|
No |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
Most - see individual statements |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
No - see Elastic jobs (preview) |
Yes - see SQL Server Agent differences |
|
|
No - see SQL Database auditing |
Yes - see Auditing differences |
|
|
Most - see individual functions |
Yes - see Stored procedures, functions, triggers differences |
|
|
Some - see individual stored procedures |
Yes - see Stored procedures, functions, triggers differences |
|
|
Some - see individual tables |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
Some - see individual views |
Yes - see T-SQL differences |
|
|
Yes. 24-GB size per vCore for entire GP tier and limited by instance size on BC tier |
||
|
Local and database-scoped global temporary tables |
Local and instance-scoped global temporary tables |
|
|
Time zone choice |
No |
Yes, and it must be configured when the SQL Managed Instance is created. |
|
No |
Yes, but only limited set of global trace flags. See DBCC differences |
|
|
Yes, in public preview. See the constraints here. |
||
|
Yes - General Purpose and Business Critical service tiers only |
||
|
Windows authentication |
No |
No |
|
No. Other techniques that provide high availability are included with every database. Disaster recovery is discussed in Overview of business continuity with Azure SQL Database. |
No. Other techniques that provide high availability are included with every database. Disaster recovery is discussed in Overview of business continuity with Azure SQL Database. |

